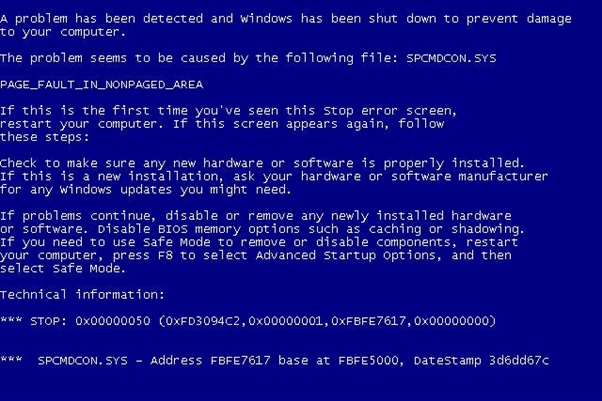
The Blue Screen of Death is an error screen in Windows that signifies a fatal system error.
BSoDs appear when Microsoft Windows encounters a critical error from which it can’t recover, usually the result of low-level software (or drivers) crashing or faulty hardware.
This forces your computer to bring up the BSoD and can cause serious problems with your computer and even loss of data
BSoDs have been present in Windows NT 3.1 (the first version of the Windows NT family, released in 1993) and all Windows operating systems released afterward.
Blue screens also look different, depending on what version of Windows you’re running.
In Windows 7 and previous versions, the blue screen looks much like a terminal screen, displaying all manner of information.
In Windows 8 and 10, blue screens of death are much simpler with few details.
What causes blue screens of death (BSoD)?
A blue screen of death occurs when Windows encounters a “STOP Error.”
This critical failure causes Windows to crash and stop working. The only thing Windows can do at that point is, restarting the computer.
BSoDs are generally caused by issues related to hardware driver software or malfunctioning hardware, such as faulty memory, power supply issues, overheating of components, or hardware running beyond its specification limits.
In some cases, though, the BSOD appears due to a corrupt operating system or hardware inside of the computer, meaning that you’ll either need to reinstall your operating system or take your computer into a tech department to have it fixed.
[ot-video][/ot-video]
Blue screen of death can sometimes be caused by issues with low-level software running in the Windows kernel.
Regular apps usually won’t be able to cause blue screens. If an app crashes, it will do so without taking the operating system out with it.
Must read: LCD TV or LED TV: Which one to buy?
If a stop error is encountered while a live kernel debugger is attached to the system, Windows will halt execution and cause the debugger to break in, rather than displaying the BSoD.
The debugger can then be used to examine the contents of memory and determine the source of the problem.
This can lead to data loss, as programs don’t have a chance to save their open data.
A BSoD can also be caused by a critical boot loader error, where the operating system is unable to access the boot partition due to incorrect storage drivers, a damaged file system or similar problems.
The BSOD is typically a result of improperly installed software, hardware, or settings, meaning that it is usually fixable.
Related:
How to access someone’s computer using Remote Desktop Connection
Samsung sales decline as Chinese companies boost market share